
A House in Multiple Occupation (HMO) is a property rented out to several unrelated individuals who form two or more separate households. These tenants share essential amenities such as kitchens and bathrooms. HMOs are regulated under the Housing Act 2004, with additional stipulations provided by the Licensing of Houses in Multiple Occupation (Mandatory Conditions of Licences) (England) Regulations 2018. Household Definition
In the context of HMOs, a household is defined as individuals who are related by family ties, including married couples, same-sex couples, and other relatives. Domestic workers, such as au pairs or nannies, living with the family are also considered part of the household.
Licensing is mandatory for HMOs that accommodate five or more occupants from at least two unrelated households. Licensing ensures that properties meet specific safety and management standards to protect the tenants’ well-being.
Local authorities have significant powers to regulate HMOs:
To obtain an HMO license, applicants must meet the “fit and proper person” criteria. This means they should not have committed serious offences such as fraud, violence, or drug-related crimes, nor should they have breached housing laws, be insolvent, or be illegal immigrants.
Following is the flowchart for a complete understanding of HMOs.
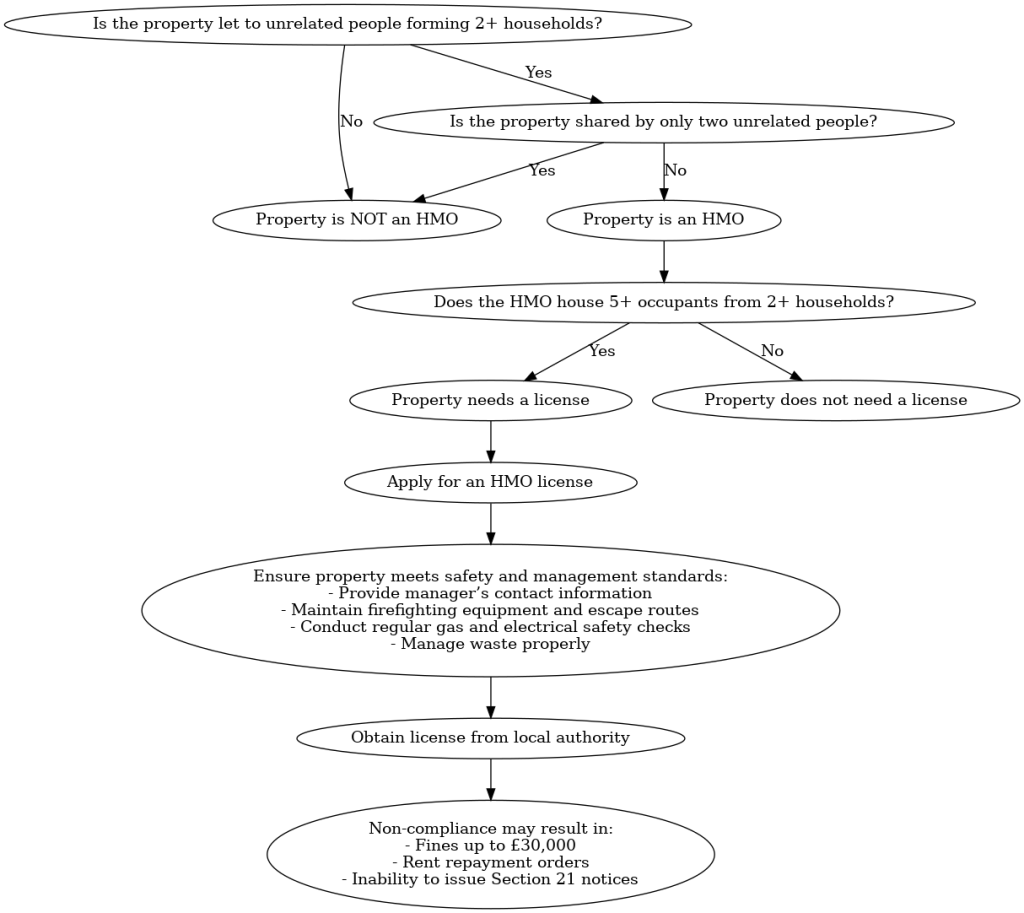
By understanding these definitions, classifications, and responsibilities, both landlords and tenants can ensure that HMOs are managed effectively, providing safe and compliant living environments.
If you are looking to optimize your property management services with ConnectX, contact us at info@connectx.live
Map
Email Us
info@connectxservices.com
Call Us
UK Office Address: 71-75, Shelton Street, London, England, WC2H 9JQ
UAE Office Address: Meydan Grandstand, 6th floor, Meydan Road, Nad Al Sheba, Dubai
©2024 ConnectX Services. All Rights Reserved.
Terms and Conditions
Privacy Policy

Subscribe to our below newsletter and never miss any update